Overcoming mental health stigma requires education, advocacy, and treatment. Through dispelling myths, encouraging candid communication, and advancing acceptance, you can provide safe spaces where people feel comfortable asking for assistance and opening up about their experiences. A concerted effort from everyone can create a society that is more caring and inclusive towards people with mental health illnesses.
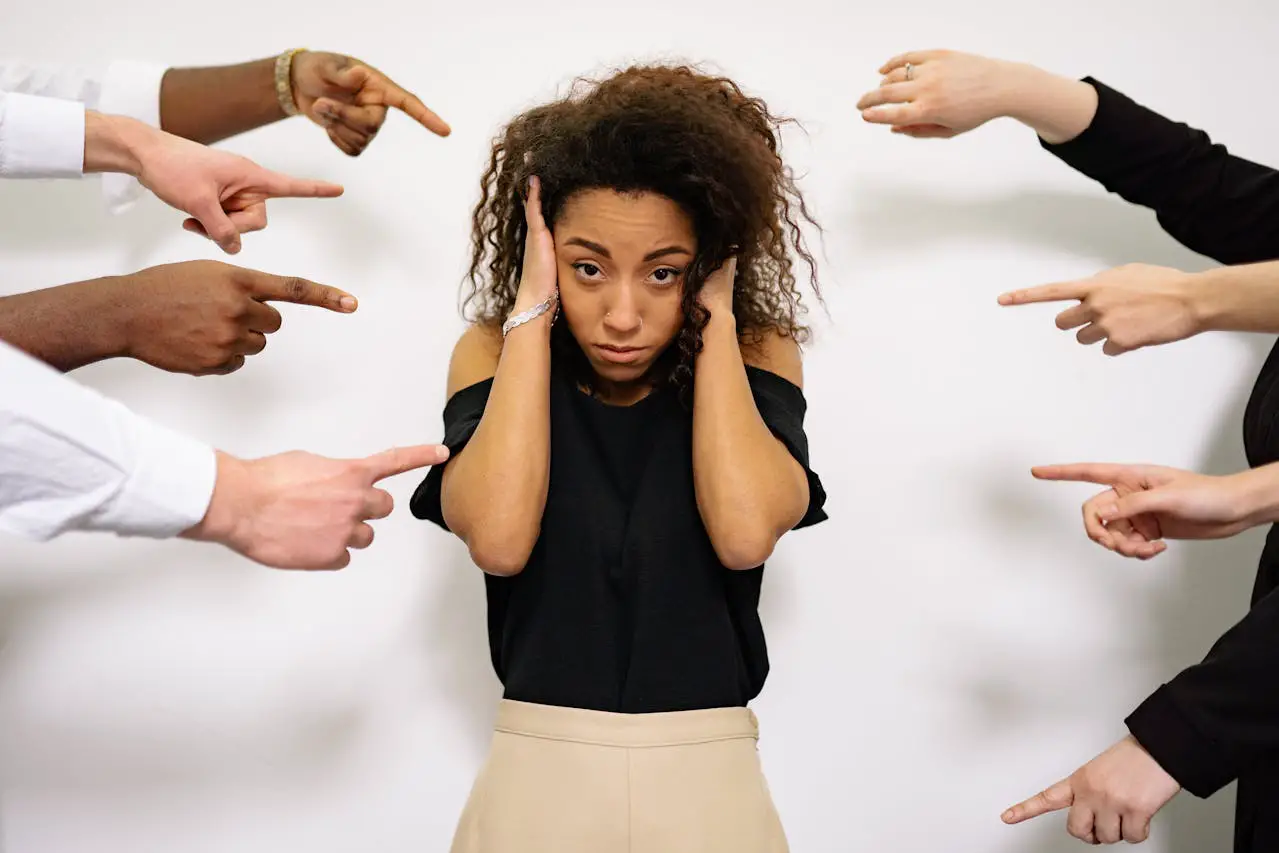
Mental health stigma is a significant obstacle to people seeking and getting treatment globally. But what is mental stigma? The term “mental health stigma” describes unfavorable attitudes, misconceptions, and ideas about mental illness. Stigma can take many forms, such as self-stigmatization, social exclusion, and discrimination in the workplace and healthcare system.
Misconceptions about mental health issues exacerbate the effects of mental illness on people and communities by fostering feelings of fear, shame, and reluctance to seek assistance. Even with increased awareness of mental health issues, many people continue to suffer in silence due to misunderstandings, prejudice, and social misconceptions.
Overcoming mental stigma has become a priority for public health worldwide. It requires coordinated efforts to promote acceptance, empathy, and understanding at the institutional, societal, and personal levels. This article will delve into overcoming mental stigma and highlight its effects.
How to Overcome Mental Stigma
Here are some ways of breaking mental health stigma.
Seek Treatment
It could be hard for you to acknowledge that you need help. Don’t let the stigma associated with mental illness keep you from getting the care you need. Treatment can bring relief by determining the cause of the problem and minimizing symptoms that affect your personal and professional life.
Proper Education
Education can help dispel myths and misconceptions regarding mental health. Promoting factual information, sharing firsthand accounts of recovery, and emphasizing the prevalence of mental illness help to reduce stigma. Public awareness and media campaigns are also essential in influencing public opinion and promoting compassion and understanding.
Promote Open Dialogue and Supportive Environments
Fostering a culture of open communication and acceptance makes it easier for people to talk freely about their experiences with mental health issues without worrying about prejudice or condemnation. Talking about mental health is crucial because it increases empathy, lessens isolation, and encourages people to seek help.
Peer support groups, counseling programs, and mental health hotlines provide secure venues for seeking support and interacting with like-minded individuals.
Don’t Let Stigma Breed Self Doubt
You may think your illness is a reflection of your weakness, but that’s not the case. Seeking counseling, learning more about your illness, and connecting with others who have mental illness can help you overcome self-judgment and boost your self-esteem.
Avoid Isolating Yourself
It’s possible that you’re reluctant to disclose your mental health condition to others. If your loved ones, friends, clergy, or neighbors are aware of your mental health condition, they can help you. Seek the empathy, understanding, and support you require from those you can trust.
Advocacy and Policy Initiatives
Advocacy plays a crucial role in breaking structural obstacles and advancing relevant policies. Legislators, mental health providers, and advocacy groups work together to promote laws that safeguard the rights of people who have mental illness, guarantee access to reasonably priced, culturally sensitive care, and make mental health services part of primary health care systems.
Seek Support
National and local organizations, like the National Alliance on Mental Illness (NAMI), provide internet resources and local activities to educate the public, families, and individuals about mental illness, therefore lowering stigma. Some federal and state agencies also have programs that offer vocational rehabilitation.
Speak up Against the Stigma
Consider sharing your thoughts on stigma in online forums, editorials, and events. When you hear someone making offensive remarks regarding mental illness, speak up. Inform others about the dangers of false, damaging stereotyping. Like everyone else, those who have mental illness ought to be acknowledged and accepted.
Types of Mental Health Stigma
There are several types of stigma associated with mental health. Let’s look at the major ones.
Self-Stigma
Self-stigma is when you believe you deserve the negative criticism and judgment from others. For instance, you might think that you’re weak because you have PTSD, which is not the case.
Public Stigma
Public stigma is society’s general opinion about those who possess a particular attribute. Media representations of these characteristics may reflect societal attitudes, often reinforcing unfavorable opinions or presenting stereotypes as reality.
Institutional Stigma
Some institutional policies are founded on stigmatizing attitudes. Even though the people who work in that organization may not be biased against you, the way the system is set up seems to target you.
Effects of Stigma on Mental Health
Mental Health stigma has various harmful effects. Here are some of them.
Reluctance to Seeking Help
The stigma related to mental illness makes it difficult to get the proper care and assistance. People may put off or refrain from asking for help out of fear of social rejection, prejudice, or judgment. This reluctance can extend suffering, worsen symptoms, and increase the risk of complications.
Social Isolation
People with mental health disorders experience social isolation and alienation as a result of stigmatizing attitudes and beliefs. The fear of humiliation makes them shy away from social engagements. This seclusion can lead to low self-esteem, loneliness, worsening symptoms of mental illness, and lower quality of life.
Self-Blame
People who are subjected to stigma related to mental health issues internalize negative misconceptions about their condition, which can lead to self-blame and diminished self-worth. Internalized anger can erode self-confidence, hinder recovery efforts, and make it difficult to ask for and accept help from others. It could also worsen depressing and dismal sentiments.
Strained Personal Relationships
The stigma around mental illness can strain connections with others and impede one’s ability to find work and progress in their profession. Stigmatizing behaviors in the workplace puts people with mental illnesses at risk of discrimination or losing their jobs. This can lead to career stagnation and inequality.
Inequalities in Access to Care
The stigma surrounding mental health makes it more difficult for some people to receive the care they need, especially in underprivileged and marginalized groups. Healthcare systems that have stigmatizing attitudes can deter people from seeking assistance. This worsens already existing social and health gaps.
Final Thoughts
To end mental health stigma, everyone must work together to dispel myths, advance knowledge and awareness, cultivate compassion and understanding, and establish welcoming and encouraging environments for those who are dealing with mental illness. We can promote mental health equity, enhance care access, and provide a more compassionate and encouraging environment for everyone by fighting stigma at all societal levels.